Introduction:
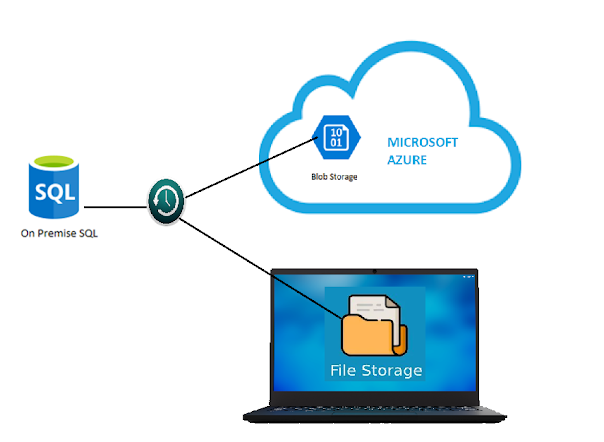
After having a successful implementation of Business Central On-Premise for the client's environment, it is necessary to automate administrative tasks such as Database Backups and restoration policies to Ensure Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery.
 |
Pre-requisites:
- Understanding of SQL Backups
-Full Backups: https://www.mssqltips.com/sqlservertutorial/7/sql-server-full-backups/
- Differential Backups:https://www.mssqltips.com/sqlservertutorial/9/sql-server-differential-backups/
- Transactional Backups: https://www.mssqltips.com/sqlservertutorial/8/sql-server-transaction-log-backups/ - Understanding of PowerShell
Demonstration:
In this blog, it is necessary that you understand the different backup types. Just to give a hint below is a one-line explanation.
i. Full Backups: Takes a full backup of DBii. Differential Backups: After the full backup takes the change in data is added to the differential backupiii. Transactional Backup: After the last backup, the transactional difference is being backed up. Ideally used for point-in-time backup.
1. Setting Up SQL Backup using Azure Blob Storage:i. Full Backups: Takes a full backup of DB
Once I log in to my SQL Server using SSMS, Goto System Databases > master > Programmability > Stored Procedures, right-click on Stored Procedure and create Stored Procedure and copy the source code below and save it with name.
Code to Backup SQL to Azure Blob storage:
1 | USE [master] |
Note: For Azure Blob storage, you also need to link your Azure Account in SSMS.
2. Setting Up SQL Backup using Local Storage:
Once I log in to my SQL Server using SSMS, Goto System Databases > master > Programmability > Stored Procedures, right-click on Stored Procedure and create Stored Procedure and copy the source code below and save it with name.
3. Creating CMD Script to call SQL Stored Procedure:
There are six different CMD scripts for Azure Blob storage, Disk storage, and types of Backup.
Each of these scripts will be stored in a .bat(BATCH) files
Azure Storage Backup:
Code to Backup SQL DB to Disk File:
1 | USE [master] |
3. Creating CMD Script to call SQL Stored Procedure:
There are six different CMD scripts for Azure Blob storage, Disk storage, and types of Backup.
Each of these scripts will be stored in a .bat(BATCH) files
Azure Storage Backup:
- Full backup:
sqlcmd -S BC\BCDEMO -E -Q "EXEC sp_Backup_Db_AzureBlob @databaseName='LS', @backupType='F'" - Differential backup:
sqlcmd -S BC\BCDEMO -E -Q "EXEC sp_Backup_Db_AzureBlob @databaseName='LS', @backupType='D'" - Transactional backup:
sqlcmd -S BC\BCDEMO -E -Q "EXEC sp_Backup_Db_AzureBlob @databaseName='LS', @backupType='L'"
Disk Backup:
- Full backup:
sqlcmd -S BC\BCDEMO -E -Q "EXEC sp_BackupDatabases_ToDisk @databaseName='LS', @backupType='F', @backupLocation='C:\DB BACKUP\'" - Differential backup:
sqlcmd -S BC\BCDEMO -E -Q "EXEC sp_BackupDatabases_ToDisk @databaseName='LS', @backupType='D', @backupLocation='C:\DB BACKUP\'" - Transactional backup:
sqlcmd -S BC\BCDEMO -E -Q "EXEC sp_BackupDatabases_ToDisk @databaseName='LS', @backupType='L', @backupLocation='C:\DB BACKUP\'"
4. Scheduling the CMD batch file to run backups recurringly:
In this case, Full Backup is scheduled once every day, Differential Backup runs every 2 hours and Transactional Backup runs every 10mins.
Below is the task scheduler created to trigger each of the scripts that we created in Step 3.
Below is the task scheduler created to trigger each of the scripts that we created in Step 3.
Conclusion:
I hope this blog helps you set up the SQL Backup policies. It is recommended that either Step 1 or Step 2 is performed to save resources. Although for additional security you can opt for both.
Also storing these backups can take up a lot of disk space, hence it is advisable to setup disk cleanup policies.
Also storing these backups can take up a lot of disk space, hence it is advisable to setup disk cleanup policies.
Feel free to comment if there are any doubts. Cheers



 Like
Like Report
Report

*This post is locked for comments