Context
Several capabilities already exist in the Microsoft Dataverse to relay events to subscribers, and a new way has been announced recently to expose events and compose business logic to respond to them asynchronously.
The main purpose of Dataverse Business Events is to allow citizen developers and professional developers to trigger business events. That is, when an action happens in one business application, other business applications can now be informed about them.
Overview
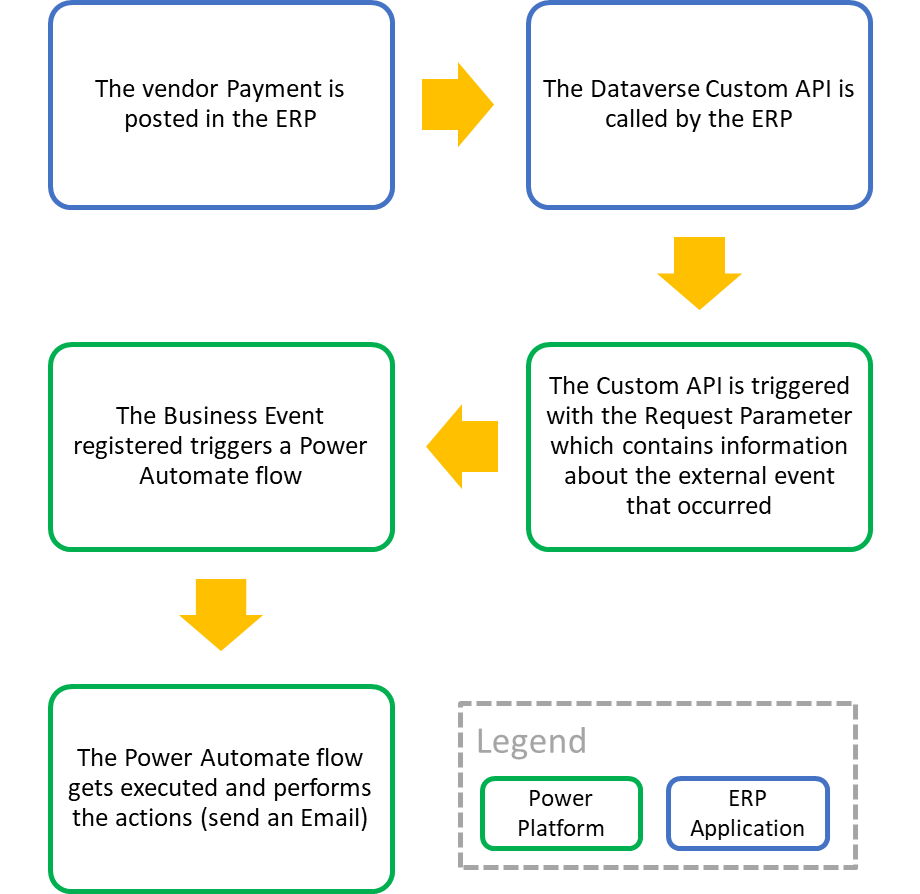
The following schema shows a high-level view of the steps that will be detailed in this article to explain how Business Events works:

- An external system calls an Action or Custom API that has been provided to trigger the Business Event.
- The Action or Custom API is triggered with the Request Parameters, which contain information about the external event that occurred.
- The action triggers the Business Event that performs some business logic asynchronously.
How does it work?
This article implements the following scenario (presented also in this documentation Microsoft Dataverse business events - Power Apps | Microsoft Docs):
You have an ERP application that has an OnVendorPaymentPosted event and you want to simplify how you centralize your automation logic. You can create a custom API representing this external event and configure the ERP application to call this Dataverse API. When you catalog this custom API as an event, you’ll be able to use the Dataverse Power Automate connector to use this event as a trigger and send an email.
For this example, it is expected nothing will be done in Dataverse except enable asynchronous logic to be registered for the event.
In order to implement this scenario, we’ll go through the following steps and considerations:
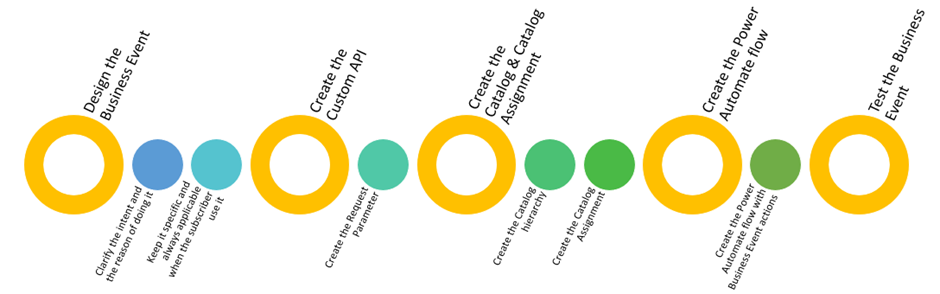
Create the Custom API
Create the Custom API with the parameter, which is Vendor ID in this example. (For more details, refer to Create and use Custom APIs (Microsoft Dataverse) - Power Apps | Microsoft Docs.)

At the end of this step, your solution should contain the following components:

Create the Catalog and the Catalog assignment
A Catalog is a structure to expose actions as business events. It’s a hierarchical structure where the top level represents a solution. (For more details, refer to Catalog and CatalogAssignment tables (Microsoft Dataverse) - Power Apps | Microsoft Docs.)
In the example, we create the Catalog with the following structure:
|
Catalog
|
Description
|
|
Contoso Manufacturing
|
Root Catalog
|
|
Contoso Manufacturing Vendors Catalog
|
2nd Level Catalog Category
|
|
OnVendorPaymentPosted Assignment
|
Catalog Assignment: Custom API
|

At the end of this step, your solution should contain the following components:

Create the Power Automate flow
- Create the cloud flow from the solution you’re working on.

- Configure the trigger by setting the Catalog, the Category, and the Action created in the previous steps.

- Configure the action, for example, by sending an email to an admin.

At the end of this step, your solution should contain the following components:

Test the Business Event
For test purposes, Postman will be used to simulate the Custom API triggering. Several community tools exist to do this. (For more details, refer to Set up a Postman environment (Microsoft Dataverse for Apps) - Power Apps | Microsoft Docs.)
- Trigger the Custom API – OnVendorPaymentPosted.

- Once the Custom API is triggered, check the run history of the Power Automate flow created previously. A new run history appears.



To conclude, Business Events can be used in several scenarios, they provide a new way to discover events and create automation when these events occur. For more details concerning the design principals and points to consider, refer to Microsoft Dataverse business events - Power Apps | Microsoft Docs



