I am going to write two articles
1st one will be how to use DevOps Pipeline to Export your solution and add it to Code Repository
2nd one will be how to Create a Release to Import your solution to various environments
As a per-requisite for this article its a good idea to familiarize yourself the various parts of DevOps, you will have a more successful implementation if you have a good knowledge of what DevOps:
Repos
Pipeline
Pipeline
Environments
Releases
Library
Task groups
Deployment groups
</> XAML are.
For this article we are going to focus more on how to Create a Pipeline, being familiar with PowerShell Script will be helpful as well.
The following documentation from Microsoft is a good reference
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/power-platform/alm/devops-build-tools
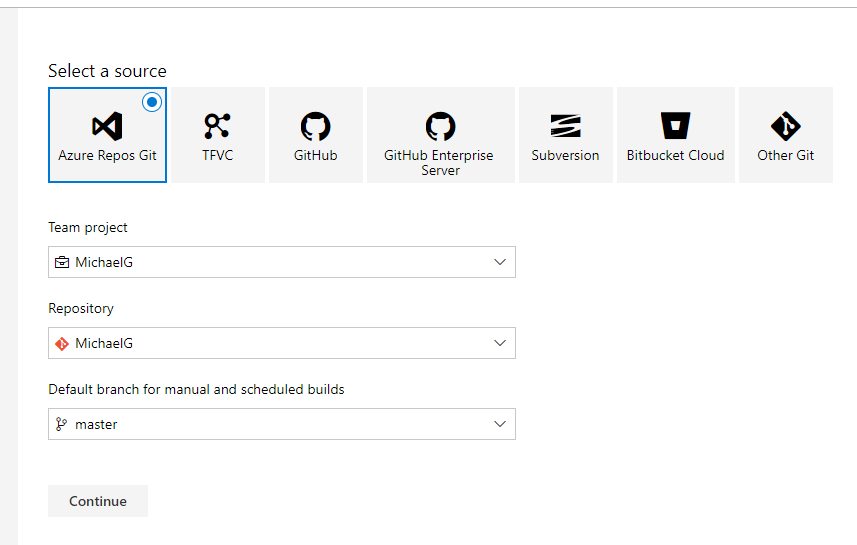
To start with Create a Folder under your Repository, in my case I called the folder “D365_Solutions”
New Pipeline
Select “Use the classic editor”
Click “Continue”
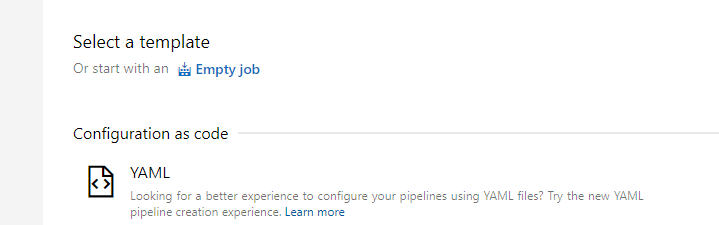
Click “Enpty Job”
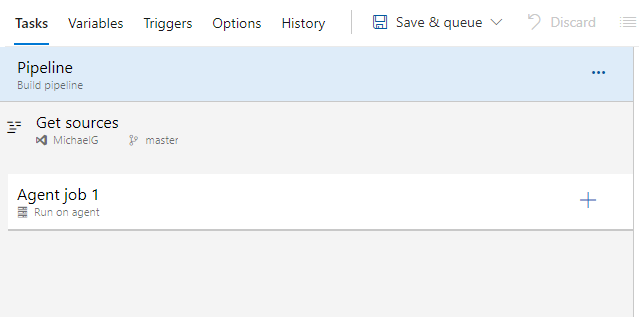
We just Created a Pipeline now what is left is
PowerShell Script to read solution Name
Use Power Platform Tool to:
Publish Customization
Increase Version
Export Solutions
Run Solution Checker
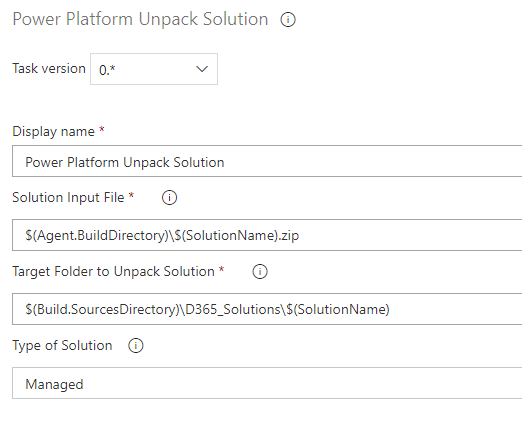
Unpack the Solutions
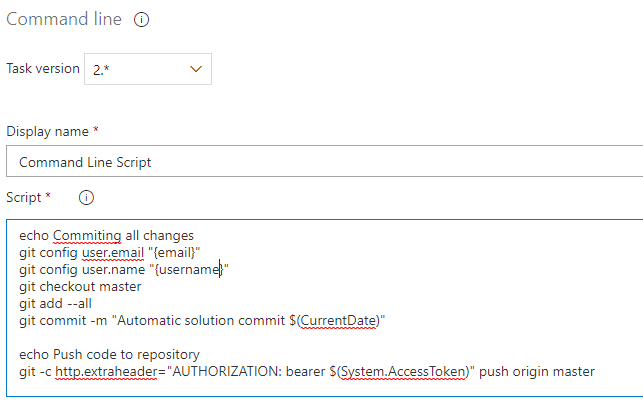
Use Command Line to Check in our Solution to the code Repository
I used a global variable under Library to store the solution Name, you can decide to store it as local variable.
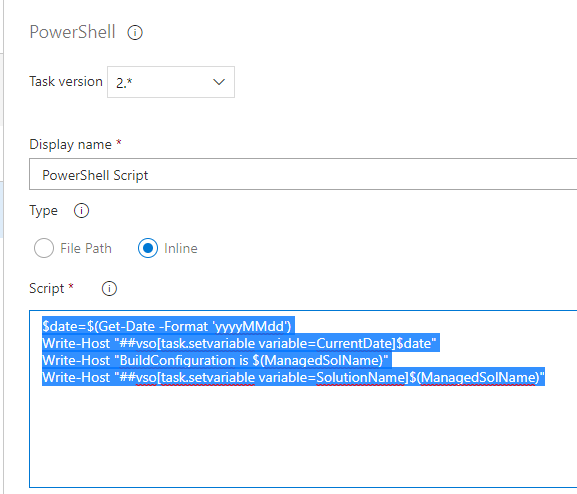
PowerShell
Code:
$date=$(Get-Date -Format 'yyyyMMdd')
Write-Host "##vso[task.setvariable variable=CurrentDate]$date"
Write-Host "BuildConfiguration is $(ManagedSolName)"
Write-Host "##vso[task.setvariable variable=SolutionName]$(ManagedSolName)"
As you can see you do not need that much knowledge of PowerShell the code is pretty much straight forward and simple
Power Platform Publish Customization
Here you have to make sure to Create your enviroments, you have two ways to do it
Username/password (no MFA support)
Service Principal/client secret (supports MFA)
I have chosen the second one “Service Pricipal/client secrete” I am sure you know how create Application user for your authentication
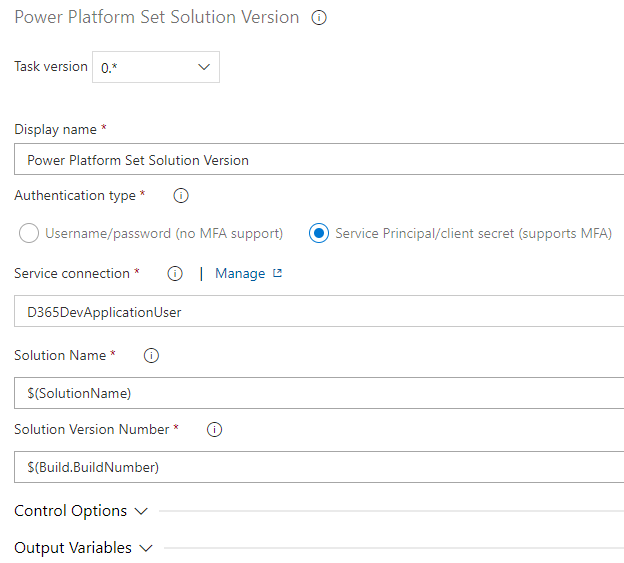
Power Platform Set Solution Version
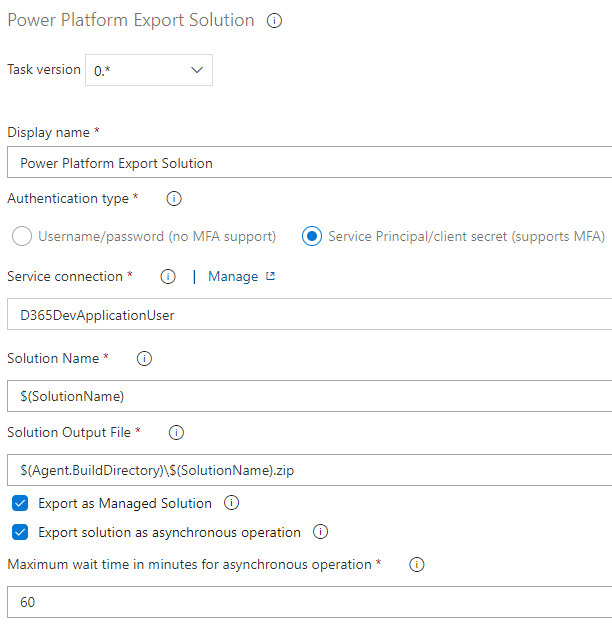
Power Platform Export Solution
One note I am exporting the solution as Managed, you have an option to work on as unmanaged too which is not ideal to deploy to upper environments like TEST, UT, PROD
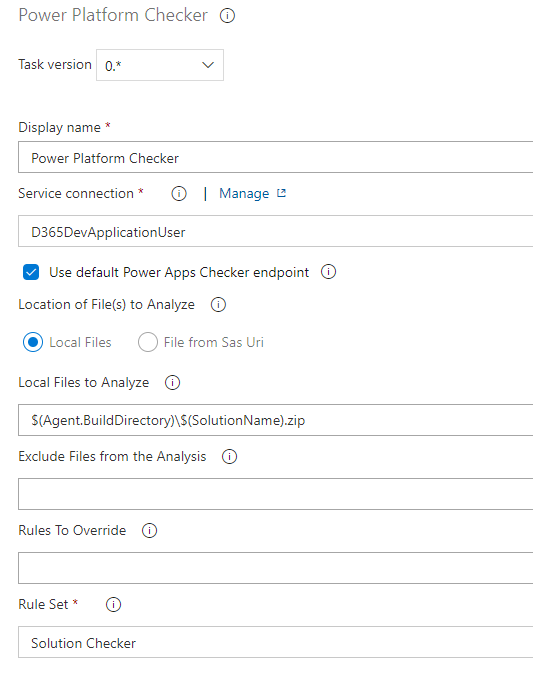
Power Platform Checker
Power Platform Unpack Solution
Command Line Check in Solution to Repository



 Like
Like Report
Report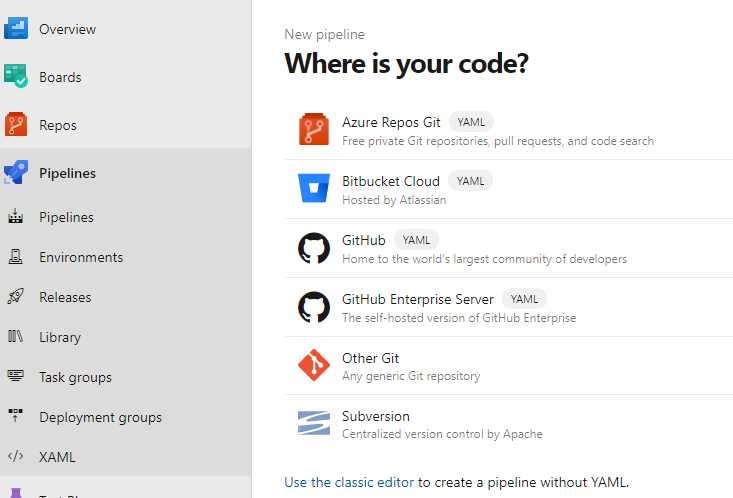


*This post is locked for comments